In 2010, a fire broke out in the engine room of the Carnival Splendor, disabling the large cruise ship, leaving thousands of passengers and crew-members stranded at sea for days. In early 2012, the Costa Concordia ran aground after its captain committed the unthinkable, which caused the death of 32 people. Despite these avoidable tragedies, and the public relations storm it found itself in at the time, Carnival Cruise Lines is reporting steady revenues and earnings.
 For 2010, Carnival reported revenues of $14.4 billions. In 2011 and 2012, revenues increased to $15.7B and $15.3B respectively. While posting very strong revenues, the company’s earnings are just as strong, posting earnings of $2.42B in 2011, followed by $1.88B in 2012.
For 2010, Carnival reported revenues of $14.4 billions. In 2011 and 2012, revenues increased to $15.7B and $15.3B respectively. While posting very strong revenues, the company’s earnings are just as strong, posting earnings of $2.42B in 2011, followed by $1.88B in 2012.
Tragedies and public relations disasters affect Carnival, and the entire cruise industry, relatively mildly compared to other businesses. Empirical data shows that the public at large, and cruise line customers have a very short collective memory when it comes to vacationing on a luxurious cruise ship. Since 2006, North American cruise passengers have steadily increased from 9.13 to 9.72 million in 2011. Worldwide in 2010, it is estimated that cruise ships were visited by 14.3 million passengers.
The question begging to be answered is, even if the public’s collective memory fades so rapidly that it does not affect traffic and consumption, why aren’t cruise lines taking a financial hit for their serious miscues? Answer is simple: Cruise lines do not respond to anyone or anything.
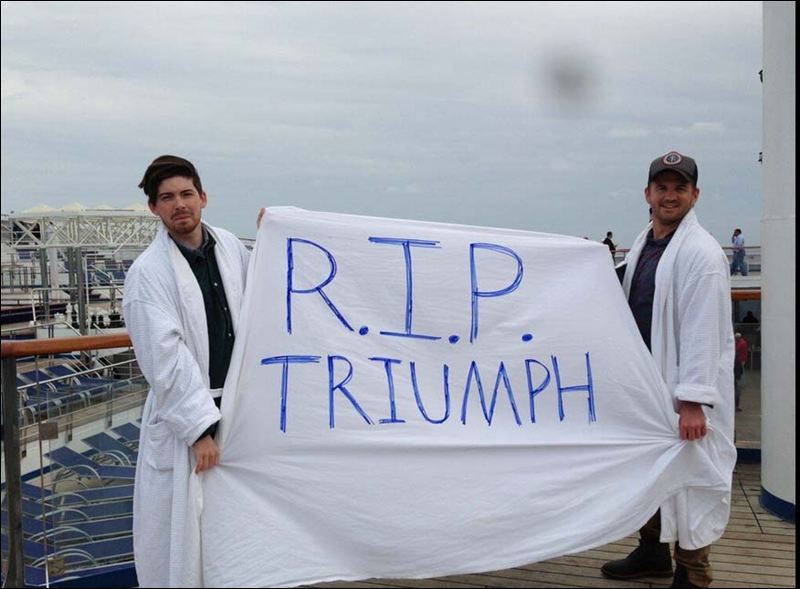
Let’s look at the thousands of passengers who were stranded aboard the Carnival Triumph for 5 days in the middle of the Gulf of Mexico. The only thing Carnival can reasonably fear is that they lost 3,143 customers for life. That is a drop in their books. The cruise line industry responds to nobody because cruise companies have handcuffed their passengers in disclaiming the cruise line’s responsibility for everything that happens on their ship, except their own negligence (46 U.S.C.A. § 30509 expressly invalidates any contract provision aiming to limit a ship’s liability for its own negligence to its passengers, but is limited to cruises visiting a U.S. port.)
Cruise lines know that their ticket-contract provisions are essentially “almighty” and have been interpreted and declared legal and binding by competent courts. Prior to embarking on the Carnival Triumph, all passengers received a ticket which contains the following:
“Carnival shall not be liable to the passenger for damages for emotional distress, mental suffering/anguish or psychological injury of any kind under any circumstances, except when such damages were caused by the negligence of Carnival and resulted from the same passenger sustaining actual physical injury, or having been at risk of actual physical injury, or when such damages are held to be intentionally inflicted by Carnival.”
Carnival also disclaims that the ship is not responsible for, and entitled to do anything its Captain decides in the event of a “breakdown of the vessel”. The ticket also contains a “Class Action Waiver” which provides that passengers waive the right to form a class action to seek recovery. In cases where the passengers only claim is a ruined vacation, class actions may be the only form of effective remedy. The legal validity of the clauses is still an open question.
Under what circumstances could a Carnival Triumph passenger sue Carnival?
Carnival can be sued if its ship committed an act of negligence that resulted in a passenger’s physical injury. For instance, if a passenger slips on urine in the middle of a hallway, and ends up fracturing a hip, Carnival can be held responsible. A passenger, who becomes physically ill from the poor conditions or contracts an illness, will also likely have a valid claim against Carnival. But the hundreds of passengers, who were “merely” subjected to sleeping on the floor with hundreds of other people in hallways flooded with urine smells and worse, will have a much more difficult time asserting claims. Although claims for so-called negligent infliction of emotional distress are allowed in certain circumstances, they are generally limited to situations where the passenger was within the “zone of danger” of physical harm and suffered an emotional injury with some physical manifestation or psychological diagnosis.
Recently, Leesfield & Partners very successfully resolved a cruise passenger claim after our client fell due to conditions caused by a fire on board a different ship that had left the vessel stranded in the middle of the ocean, thereby creating an unstable platform for walking.
Continue reading
 Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog
Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog